Hits: 647 img
Polysilazane (PSZ) is a type of inorganic polymer with a main chain composed of repeating Si-N bonds. The following is a detailed introduction to polysilazane:
I. Classification and Structure
Polysilazanes can be classified into cyclic polysilazanes, oligomeric polysilazanes, and high-molecular-weight polysilazanes based on their molecular structures. They can also be divided into inorganic polysilazanes (such as perhydropolysilazane) and organic polysilazanes (such as methyl, vinyl, fluorine-containing, and heteroelement-modified ones) based on their functional groups. Their molecular structures primarily contain silicon, nitrogen, and carbon elements, hence they are also known as silazane polymers.
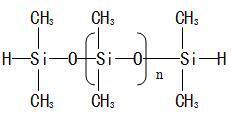
II. Properties and Characteristics
Polysilazanes exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, radiation resistance, and high-temperature resistance. After curing, their hardness can reach 8H or above, and they can be converted into SiCNO, SiCN, or silicon dioxide ceramics under high-temperature conditions. Additionally, polysilazanes combine the plasticity and processability of organic materials with the high thermal stability, high dielectric strength, electrical resistivity, low thermal conductivity, and flame retardancy of inorganic materials.
III. Synthesis and Applications
The synthesis methods of polysilazanes include ammonolysis, aminolysis, hydrazinolysis, ring-opening polymerization, dehydrogenative coupling, and others. As research continues to deepen, the number of synthesis methods for polysilazanes is increasing. In terms of application fields, polysilazanes have wide applications in aerospace, semiconductors, photovoltaic cells, high-temperature-resistant coatings, ceramic materials, resin materials, and other areas. Especially in the fields of new energy and electrical power, the high dielectric strength and electrical resistivity of polysilazanes make them ideal insulating materials.
IV. Market and Challenges
The global market size of polysilazanes is growing annually, but the preparation technology is challenging, and the reaction products have complex compositions, leading to high production costs. Furthermore, polysilazanes have high reactivity towards water, heat, oxygen, and polar compounds, making storage and transportation difficult. These factors limit the further promotion and application of polysilazanes.
In summary, polysilazane, as a new cutting-edge material, has broad application prospects and development potential.
More details please click here.